How to execute Python code in Google Colab
Google Colab is a browser-based application for writing and executing code. It does not require you to install Python or individual packages on your local machine. This is why it is particularly handy for first-time users of Python and for people with less powerful computers.
Sign up for Google Drive to use COLAB
To be able to use Colab, you will need a Google account. If you do not have one or do not want to use your own, please sign up for a dummy address. Of course, GOOGLE is a proprietary service and not GDPR-compliant, so do not bring data that contain personal information, e.g. customer names, phone numbers or private mail addresses. In the future, I will be able to offer workshops using the university DSRI or a code-hosting platform provided by The Plant.
Create a folder for your code and data
On the
Adding the correct file path to your script
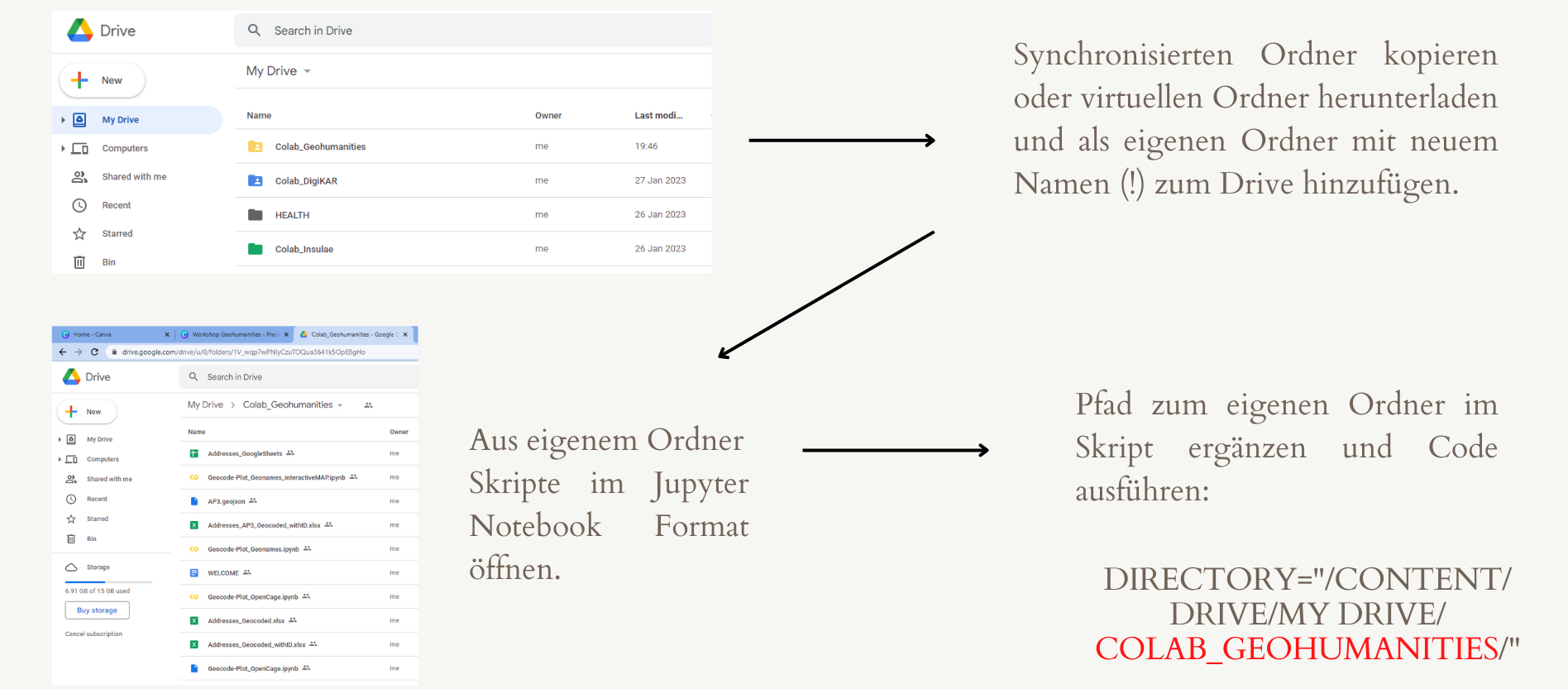
Whenever you upload files to your Google Drive on the top level, the standard path is "/content/drive/My Drive/".
Any subfolders you create will have to be linked as "/content/drive/My Drive/YourFolder/".
Please make sure to change all instances of file paths in scripts you download from Github according to this pattern.
Similarly, participants of my workshops who have direct access to one of my Google Drive Colabs should copy that folder to create their own instance and also change file paths where necessary.</p>
This German screenshot summarises the workflow for copying a shared Colab folder to your own Drive:
Executing code in Colab
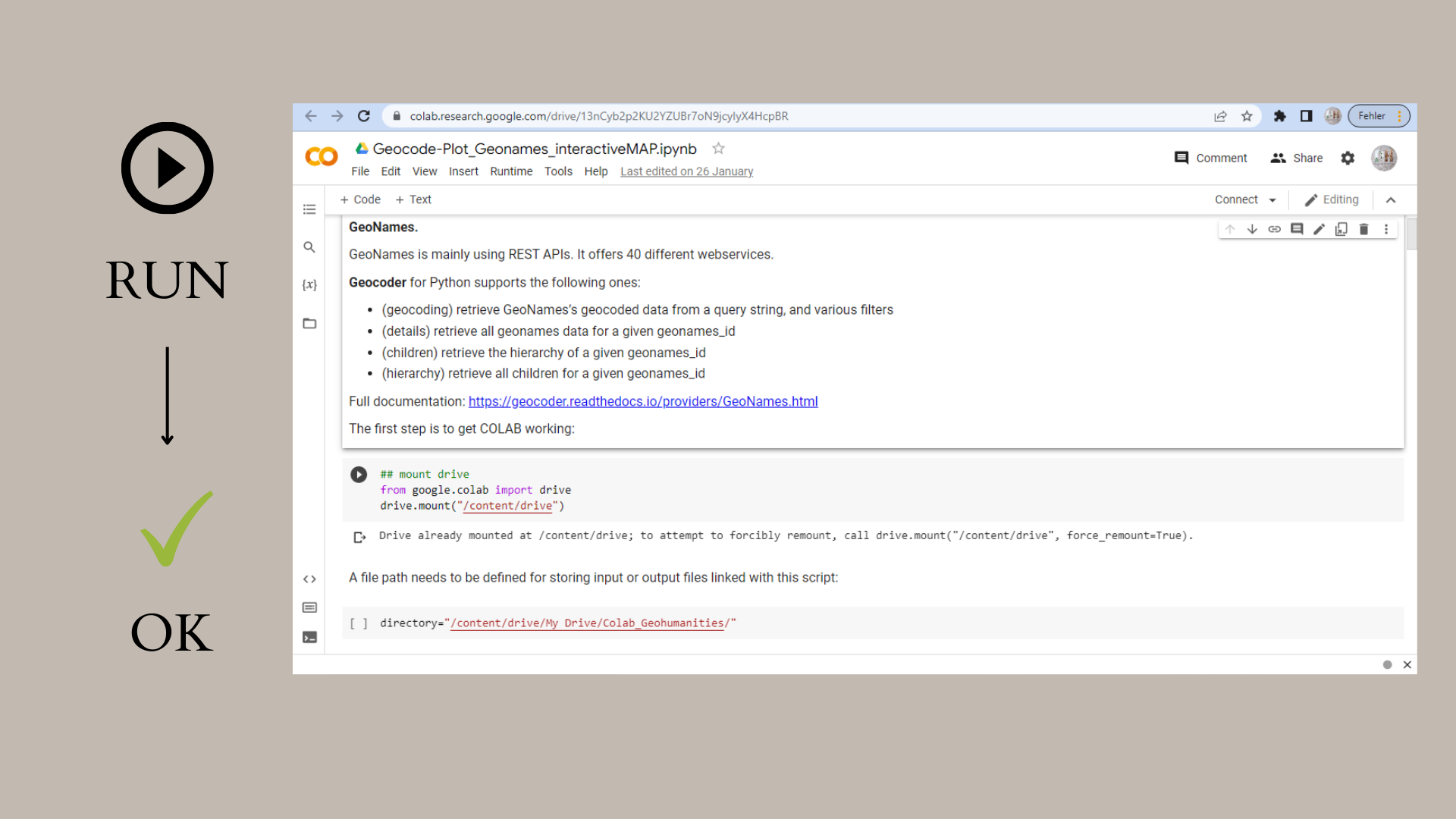
Code provided in Colab mostly comes in Jupyter Notebook format and combines the actual code with explanations. The explanations are meant for the user but are not part of the actual script. The code that can be executed normally has a grey background and a little "play" button in the top-left corner. Each section of code has to be run one after the other. A green arrow on the left hand side indicates if a section of code has been executed correctly. Please see the instructions in the screenshorts below.
Common compatibility issues
When using Jupyter Notebooks in Google Colab, compatibility issues can arise, especially when using interactive widgets or language-specific resources that are no longer available or supported. Jupyter widgets like those I use for plotting map can cause a notebook to crash or become unreadable in Colab. When updating my Colab code for the last time, I have tried to fix this issue by stripping any “widgets” metadata from the notebook, but please let me know if new errors occur. For user interaction, I prefer file upload and download functions in Colab to avoid widget use where possible. Another common issue but one that is not restricted to Colab is a version mismatch between package dependencies. Moreoever, session timeouts or memory limits in Colab can occur when running more extensive operations. If possible, run code locally or in an institutional environment with more resources and better support. Where this is not an option, you may want to work with sampled or chunked data and process them iteratively. Also, avoid hard-coding links to resources that might disappear. Finally, encoding issues (e.g., UTF-8 vs Latin-1) frequently affect data processing with code. Especially when you are working with non-English data, this can trigger errors.